Have you ever wondered what makes some glow-in-the-dark watches and signs shine so brightly without batteries? The answer lies in something called Tritium.
This tiny element plays a powerful role in lighting up objects safely and efficiently. If you want to understand what Tritium is and why it matters to you, keep reading. By the end, you’ll see how this little-known substance impacts everyday life in surprising ways.

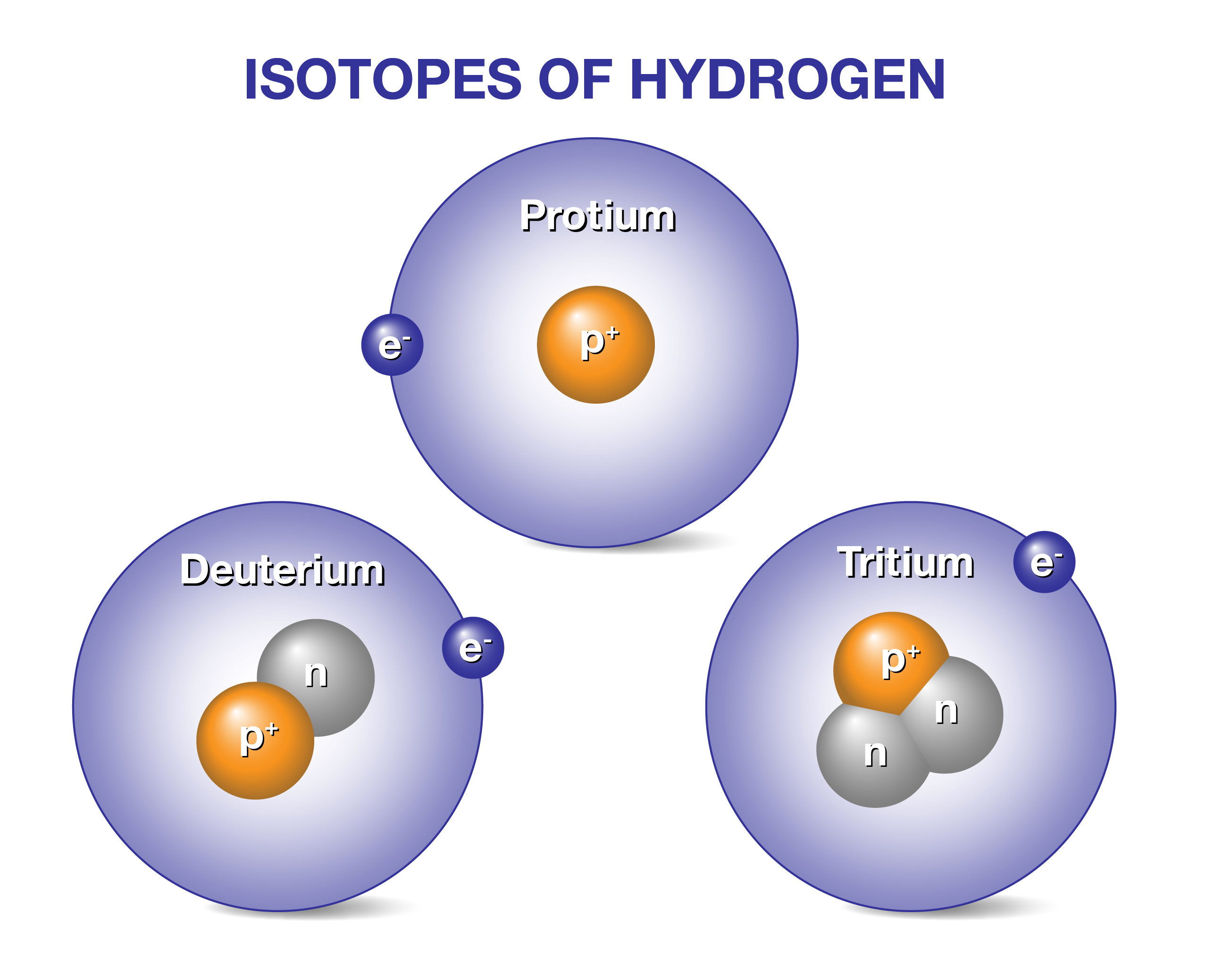
Tritium Basics
Tritium is a rare and special type of hydrogen. It plays a key role in science and technology. Understanding its basics helps us learn why it matters.
This section explains what tritium is made of, where it is found, and how it is made.
Atomic Structure
Tritium is a hydrogen isotope. It has one proton and two neutrons. This makes it heavier than normal hydrogen. Its atomic number is 1, just like hydrogen. The extra neutrons make it unstable and radioactive. It slowly breaks down over time.
Natural Occurrence
Tritium is very rare in nature. It forms when cosmic rays hit the Earth’s atmosphere. This process creates small amounts of tritium. It mixes with water and air. Plants and animals take it in. Natural tritium levels are low and hard to detect.
Production Methods
Most tritium used today is man-made. Nuclear reactors produce it by bombarding lithium or heavy water. Particle accelerators can also create tritium. These methods produce tritium for research and industry. Controlled production keeps tritium available for many uses.
Unique Properties
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen with special features. These unique properties make it useful in science and industry. Understanding these traits helps explain why tritium is valuable.
Radioactive Characteristics
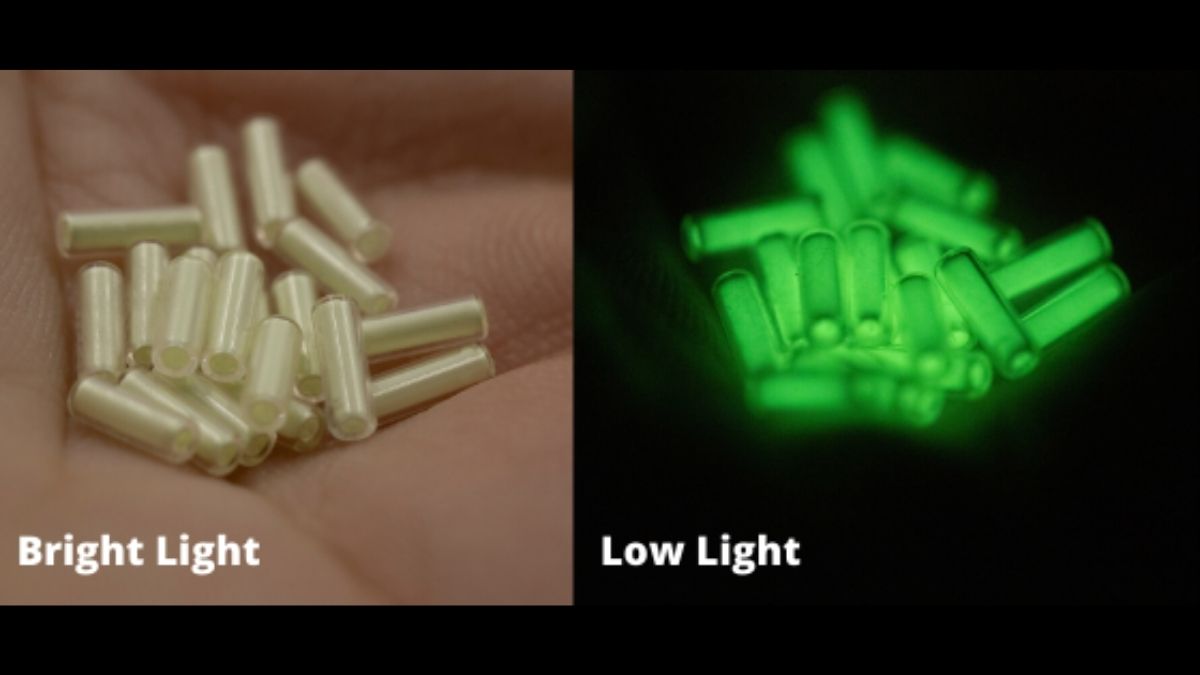
Tritium is radioactive. It emits low-energy beta particles. These particles cannot pass through the skin. This makes tritium safer than many other radioactive materials. It glows faintly in the dark when combined with phosphors. This glow is used in watch dials and exit signs.
Half-life And Decay
Tritium has a half-life of about 12.3 years. This means half of it decays in that time. It slowly turns into helium-3 gas. The decay process releases a small amount of energy. Because of this, tritium does not last forever but remains useful for years.
Physical And Chemical Traits
Tritium behaves like normal hydrogen in most ways. It can form water, called tritiated water. This water is slightly radioactive. It is heavier than regular water due to extra neutrons. Tritium gas is colorless and odorless. It mixes easily with air and other gases.
Applications Of Tritium
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen with special uses. It has unique properties that make it valuable in several fields. Understanding where tritium applies helps to see its importance.
Nuclear Fusion Energy
Tritium plays a key role in nuclear fusion. Fusion is a process that powers the sun. Scientists try to use fusion to create clean energy on Earth. Tritium fuels fusion reactors because it reacts easily with deuterium. This reaction releases a lot of energy without harmful emissions.
Self-luminous Devices
Tritium glows without light or electricity. This makes it perfect for self-luminous devices. It is used in watch dials, exit signs, and gun sights. These devices stay visible in the dark for many years. Tritium’s glow is safe and lasts a long time.
Scientific Research
Scientists use tritium to trace chemical and biological processes. It helps track water movement in the environment. Researchers also study how materials change over time using tritium. This helps improve products and understand natural systems better.

Safety And Environmental Impact
Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen. It is used in various industries, including nuclear energy and lighting. Understanding its safety and environmental impact is important. This helps people know how to handle tritium safely and protect nature.
Radiation Risks
Tritium emits low-energy beta radiation. This type of radiation cannot penetrate human skin. It becomes dangerous if tritium enters the body. Inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption can cause harm. The risk is low but still important to control.
Handling And Storage
Tritium must be stored in sealed containers. These containers prevent leaks and limit exposure. Workers use protective gear when handling tritium. Strict safety rules guide its transport and storage. These steps reduce the chance of accidents.
Environmental Concerns
Tritium can enter water sources if not controlled. It mixes with water and spreads easily. This may affect plants, animals, and humans. Careful monitoring and cleanup are needed to protect the environment. Regulations help limit tritium release into nature.
Future Prospects
The future of tritium holds many possibilities. This rare isotope plays a key role in energy and science. Its demand may rise due to new technologies and uses. Understanding these future prospects helps us see tritium’s growing importance in the world.
Advancements In Fusion Technology
Fusion technology aims to create clean and abundant energy. Tritium is vital for fusion reactions. Scientists work to improve how fusion reactors use tritium. Better methods may increase energy output and safety. These advances could make fusion power more practical and widespread.
Potential New Uses
Tritium’s unique properties open doors to new applications. It could help in medical imaging and treatments. Environmental sensors using tritium might detect pollution more effectively. Military and space fields may find fresh uses for tritium. Research continues to explore these possibilities.
Global Supply And Demand
Currently, tritium supply is limited and controlled. Demand may grow with fusion energy and other uses. Countries compete to secure steady tritium sources. Production methods might expand to meet future needs. Balancing supply and demand will shape tritium’s market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Tritium And Its Basic Properties?
Tritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen with one proton and two neutrons. It emits low-energy beta radiation and has a half-life of about 12. 3 years. Tritium occurs naturally in trace amounts but is mostly produced artificially for scientific and industrial use.
How Is Tritium Produced And Where Is It Found?
Tritium is mainly produced in nuclear reactors by neutron bombardment of lithium or heavy water. It is also formed naturally in the upper atmosphere through cosmic ray interactions. Industrially, tritium is used in self-luminous devices, scientific research, and fusion energy experiments.
What Are The Common Uses Of Tritium Today?
Tritium is used in glow-in-the-dark watches, exit signs, and gun sights due to its radioluminescence. It also plays a key role in nuclear fusion research and serves as a tracer in environmental studies. Its unique properties make it valuable for both commercial and scientific applications.
Is Tritium Safe For Human Exposure?
Tritium emits weak beta radiation, which cannot penetrate skin. However, internal exposure through ingestion or inhalation can be harmful. Safety protocols limit exposure levels, making controlled use safe for workers and the environment when handled properly.
Conclusion
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen with unique properties. It plays a key role in science and energy. People use tritium in medical, industrial, and research fields. Its ability to glow without power makes it useful for safety signs.
Understanding tritium helps us learn about nuclear reactions and energy sources. Though it is radioactive, careful handling keeps it safe. Tritium remains an important subject in science and technology today.
Apply for this vacancy
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.

