Have you ever wondered what makes tritium so unique in the world of elements? Understanding the tritium atomic number is the key to unlocking its special place in science and technology.
Whether you’re curious about how it works or why it matters to your daily life, this article will give you clear and simple answers. Keep reading to discover fascinating facts about tritium that could change the way you see the elements around you.
Tritium Basics
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen with unique properties. It plays a key role in science and industry. Understanding its basics helps explain its importance.
This section covers the atomic number of tritium and its place among hydrogen isotopes. Simple explanations make these concepts clear.
Atomic Number Significance
The atomic number of tritium is 1. This number shows how many protons are in its nucleus. Every hydrogen atom, including tritium, has one proton.
The atomic number defines an element’s identity. Tritium’s atomic number confirms it is a hydrogen isotope. The difference lies in the number of neutrons.
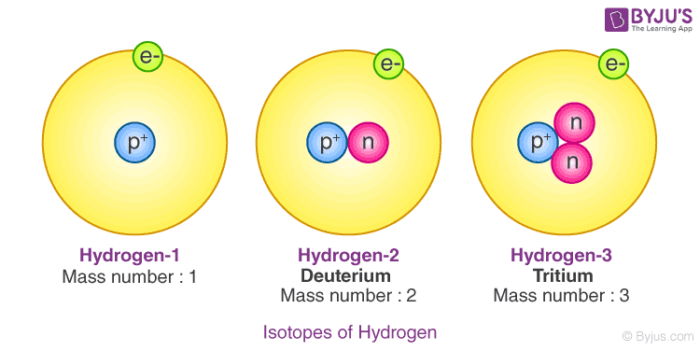
Isotopes Of Hydrogen
Hydrogen has three main isotopes: protium, deuterium, and tritium. They all share one proton but differ in neutrons.
Protium has zero neutrons, deuterium has one, and tritium has two neutrons. This makes tritium heavier than other isotopes.
Tritium is radioactive and less common than the other two. Its unique neutron count gives it special traits for scientific use.

Nuclear Structure Of Tritium
The nuclear structure of tritium is a key topic in understanding this isotope of hydrogen. Tritium has unique properties due to its nucleus. Its nucleus holds particles that determine its behavior and stability.
Studying tritium’s nucleus helps explain its radioactive nature. It also reveals why tritium is useful in scientific and industrial fields. The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons arranged in a specific way.
Protons And Neutrons Count
Tritium’s nucleus contains one proton. This proton defines it as a hydrogen isotope. Along with the proton, tritium has two neutrons. These neutrons add to the nucleus mass but carry no charge.
The total number of protons and neutrons is three. This makes tritium heavier than regular hydrogen. The extra neutrons cause tritium to behave differently in reactions.
Nuclear Stability Factors
Tritium’s nucleus is unstable due to its neutron count. The two neutrons create an imbalance with the single proton. This imbalance causes tritium to decay over time.
Radioactive decay happens as tritium tries to reach stability. It emits particles and energy during this process. The half-life of tritium is about 12 years.
External factors like environment and energy states can affect stability. The weak nuclear force also plays a role in decay. Understanding these factors helps in using tritium safely.
Radioactive Properties
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen with unique radioactive properties. It is unstable, meaning it changes over time by releasing energy. This energy release happens through a process called beta decay. Tritium’s radioactivity is important in science and industry. Its behavior helps us understand nuclear physics and radiation safety.
Beta Decay Process
Tritium undergoes beta decay by emitting a beta particle. This particle is a high-energy electron. During decay, a neutron in the tritium nucleus turns into a proton. This changes tritium into helium-3. The emitted beta particle carries away energy. It can penetrate materials but is stopped by thin layers. This process is slow and steady. It is the main reason tritium is radioactive.
Half-life Characteristics
Tritium has a half-life of about 12.3 years. Half-life means the time taken for half of a sample to decay. This period is long enough for many uses. It is short enough for tritium to change measurably over decades. Scientists use this half-life to measure the age of objects. It also helps in tracing water movement and other environmental studies. The steady decay rate makes tritium useful in many applications.
Applications Of Tritium
Tritium is a rare form of hydrogen with unique properties. Its applications span many fields. People use tritium for energy, lighting, and science. Understanding these uses helps us see its importance.
Uses In Fusion Energy
Tritium plays a key role in fusion energy research. Fusion is the process that powers the sun. Scientists try to recreate fusion to produce clean energy. Tritium acts as fuel in fusion reactors. It combines with deuterium to release large amounts of energy. This fuel helps generate power without harmful emissions.
Role In Radioluminescence
Tritium is widely used in radioluminescence. It emits low-energy beta particles. These particles cause phosphors to glow without electricity. This glow is useful for watch dials and exit signs. It provides light in dark places without batteries. The glow lasts for many years, making it reliable.
Tracer In Scientific Research
Scientists use tritium as a tracer in research. It helps track chemical and biological processes. Tritium can label water molecules or other substances. Researchers follow its path to study movement and reactions. This method reveals important information about the environment and medicine.
Safety And Environmental Impact
Tritium is a radioactive form of hydrogen with an atomic number of 1. It has unique uses but also requires careful handling. Understanding its safety and environmental impact is important for everyone.
Tritium emits low-energy radiation. This radiation can be harmful in large amounts. Protecting people and the environment is key when working with tritium.
Radiation Exposure Risks
Tritium mainly gives off beta radiation. This radiation cannot pass through skin. The main danger is if tritium enters the body. It can happen by breathing, swallowing, or skin contact with tritiated water.
Inside the body, tritium may cause damage to cells. The risk depends on how much tritium is absorbed. Small amounts usually cause little harm. Long-term exposure to high levels can increase cancer risk.
Containment And Disposal
Tritium must be stored in sealed containers. These containers stop the release of radioactive gas or water. Facilities handling tritium have strict rules to prevent leaks.
Disposal of tritium waste follows government regulations. It often involves dilution or storage until the radiation fades. Safe disposal helps protect soil and water from contamination.
Future Research Directions
Research on tritium and its atomic number is growing. Scientists explore new ways to use this isotope in science and technology. This research helps us understand nuclear processes and develop new tools. The future holds exciting possibilities for tritium studies.
Advancements In Nuclear Science
Scientists study tritium to learn about nuclear reactions. Research on tritium helps improve fusion energy experiments. Tritium’s behavior under different conditions is a key focus. This work could lead to safer and cleaner energy sources. Better knowledge of tritium helps monitor nuclear materials and reduce risks.
Potential Technological Innovations
Tritium may play a role in new lighting and battery technologies. It is used in self-powered light sources for safety and navigation. Researchers explore tritium to improve these devices. Future tech could include longer-lasting, low-energy lights. Tritium’s unique properties offer many chances for new inventions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Atomic Number Of Tritium?
Tritium has an atomic number of 1, the same as hydrogen. It contains one proton in its nucleus, defining its atomic number.
How Does Tritium Differ From Regular Hydrogen?
Tritium is a hydrogen isotope with two neutrons. Regular hydrogen has no neutrons, while Tritium has one proton and two neutrons.
Why Is Tritium’s Atomic Number Important?
The atomic number identifies Tritium as hydrogen. It determines chemical properties and its place on the periodic table.
Can Tritium’s Atomic Number Change?
No, Tritium’s atomic number cannot change. It always has one proton, which defines it as hydrogen.
Conclusion
Tritium has an atomic number of 1, like hydrogen. It contains one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. This makes it a rare and interesting isotope of hydrogen. Tritium plays an important role in science and energy research. Understanding its atomic number helps explain its behavior and uses.
Knowing these facts makes tritium easier to understand. It shows how small changes in atoms can affect their properties. Tritium’s unique features make it valuable for many studies. It reminds us of the diversity in the world of atoms.
Apply for this vacancy
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.
For more information
For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to assist with any questions or provide additional details to help you make informed decisions. Reach out today, and let’s connect!
Please mention the respective article number.

